(photo from https://www.team-cymru.com/)
Due to the solemnity of the recently discovered security loopholes (stated subsequently), 2014 is nominated to be the year of credential theft, online payment fraud and privacy violation.
History - One week ago:
Knowing that GnuTLS is an open source library and its code was written in 2005, many eyes missed the bug for almost 10 years - not being exploited in the wild is out of all expectations.
A bit of math A + B = ?
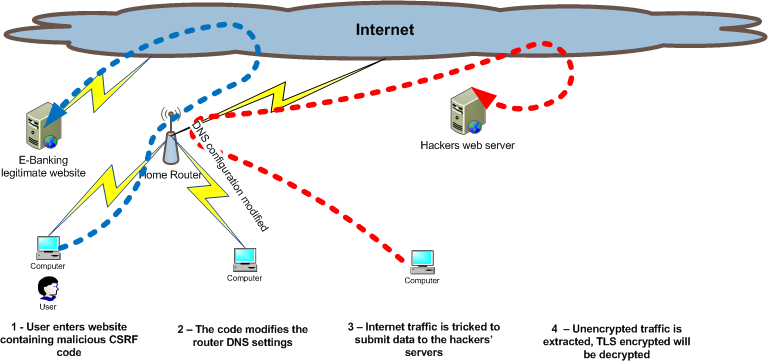
Attack anatomy:
What to do ?
- Install DD-WRT on your router: DD-WRT an open source third-party firmware, opensource means less risks since code is securely reviewed by the community. DD-WRT is designed to replace the original firmware on some commercial routers. Alternative firmware may offer features and functionality sets that differ from the original firmware it is replacing. (As an alternative, Buffalo Wifi router offers DD-WRT firmware off-the-shelf)
- If Point#1 wasn't possible, change all your passwords - use different strong ones for each account, don't reuse old and new ones.
- Update your router firmware to the latest version - change the administrator default password and disable default existing users for telnet such as `user/user'.
- Sadly, lots of ISPs lock down their routers preventing you from 'fixing' or 'reconfiguring' - contact them asking for security upgrades or take your router back by force hacking it by yourself yourself (do it at your own risk!)
- Back up your blog and websites. Do it on encrypted channels such as SSL/TLS (weak-encryption is better than no-encryption after all). Keep a local copy for your backup files.
- Refrain from using FTP to your server - replace it by sFTP or FTPs - change your old ftp passwords.
- Try as much as possible to use applications that support 2nd layer of encryption.
- Stop using Whatsapp, replace it by Telegram, TextSecure or CryptoCat for Mobile (recently released for iOS and soon for Android) - the stated mobile apps support `strong 2nd layer of encryption` besides SSL/TLS.
- Keep your operating systems up to date by enabling `security` automatic updates.
- Always monitor your DNS configuration at the router level.
- Use web antivirus that scans your browser's transiting data for attacks such as XSS and XSRF.
Generic Closure:
SSL is being phased out for known weaknesses and TLS is there to replace it. Gerenerally, we got used to having a backup service each and every time a well known and relied-on service gets compromized, this time and considering all over the world monitoring systems, I find internet stuck - security is a double edged sword. We always tend to top-up and patch our existing ideas for improvement, but `problems cannot be solved at the same level of thinking that created them` - it's time to think different, maybe encrypting on a different level? maybe moving the internet to different medium? Internet 2.0 ? an alternative for internet ? "Alternet" seems an nice fictional idea, we all tend to believe in beautiful thoughts that make us `feel` secure.
Very interesting and possibly related links:
Growing exploitation of small office routers creating serious risks <--- A MUST READ !
Reference for GnuTLS patch (for system and security administrators)
Downloading SSH client safely is almost impossible
A crypto challenge for Telegram developpers
Should we all have something to hide?
GNU security library GnuTLS fails on cert checks: Patch now
iOS goto fail
Crytpoweakness in Whatsapp
Hackers hijack 300,000-plus wireless routers, make malicious changes
Python interface for WhatsApp


Leave a comment!